Have you ever wondered why so many seniors have knee pain? They often think it’s just part of getting older. But tendonitis in seniors is a common problem that’s often overlooked and misdiagnosed. As you get older, your joints wear out, leading to tendon inflammation and pain.
It’s important to know how tendonitis affects older adults. This article will cover symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. You’ll learn how to tackle this common issue.
Key Takeaways
- Tendonitis is a significant contributor to knee pain in elderly individuals.
- Symptoms of tendonitis are often misdiagnosed as arthritis, leading to inadequate treatment.
- Non-surgical options for treating knee tendonitis show high success rates in older adults.
- Engaging in regular low-impact exercise can reduce the risk of developing tendonitis.
- Understanding the importance of tendon health is key for maintaining mobility as you age.
Understanding Tendonitis
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is when inflammation of tendons happens. Tendons are important tissues that connect muscles to bones. This issue is common in seniors, and knee tendonitis is a big problem.
The knee is a key joint that bears weight. It’s prone to stress and overuse, causing pain and mobility issues.
Seniors with chronic tendon pain may face discomfort for months. This pain can hit different areas, like the elbow, shoulder, heel, hip, and knee. As people get older, their tendons get stiffer and less flexible, raising the risk of knee tendonitis.
Knowing about tendonitis is important. It can really affect how seniors live their daily lives.
Many seniors do exercises that can hurt their tendons. Running, jumping, and even simple activities can lead to knee tendonitis. Being overweight, not moving much, and being older also increase the risk.
Spotting knee tendonitis early is key to preventing it from getting worse. Treatment often includes rest, ice, and pain meds. But, if pain doesn’t go away, seeing a doctor is a good idea.
Common Symptoms of Tendonitis in Seniors

Tendonitis can really affect seniors, causing pain and limiting their activities. You might feel pain, stiffness, and swelling near the joint. These symptoms often get worse when you’re active or after sitting for a long time.
Seniors with tendonitis might feel pain in one spot, but it can spread to other areas too. Over 70% of people with this condition say they feel pain when they move. They also notice swelling and sometimes a grating feeling.
As people get older, tendonitis becomes more common. It affects between 30% and 50% of older adults. This is because tendons get weaker and less flexible with age. This makes tendonitis more likely, mainly due to repeated movements or sudden injuries.
It’s important to know the signs of tendonitis early. Spotting it early helps in getting the right treatment. This can help with knee pain relief for seniors and stop things from getting worse. If you have ongoing pain or swelling, see a doctor. It’s key if it’s making it hard to move or enjoy life.
Causes of Knee Tendonitis in Seniors
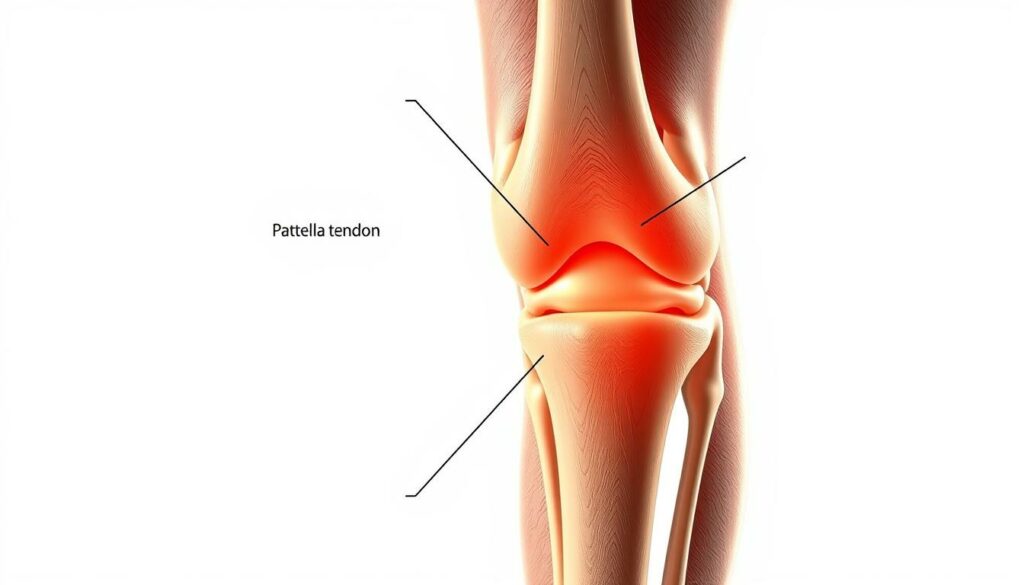
Knee tendonitis in seniors often comes from aging and overuse. As we get older, our knees wear down. This makes them more likely to get hurt. Simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs can make knee pain worse.
Being overweight is another big risk. People who are overweight are 2-3 times more likely to get knee tendonitis. If you’ve had knee injuries before, you’re at even higher risk. Activities that involve a lot of impact can also cause knee tendonitis seniors.
Other health issues, like osteoarthritis, also play a part. About 30% of seniors over 65 have knee osteoarthritis. This can lead to tendonitis. Knowing these risks can help you take steps to protect your knees.
Tendonitis in Seniors: How It Affects The Knees

Knee tendonitis can make simple tasks hard and affect your life quality. It can make walking, bending, or standing painful. This pain can stop you from doing things you love, affecting your mood and happiness.
Impact on Daily Activities
Dealing with tendonitis in seniors means living with pain that gets in the way. Simple tasks like climbing stairs or walking can be tough. This pain can make you feel frustrated and helpless.
Many seniors change how they do things to avoid pain. But, these changes can lead to more problems in the future.
Long-term Effects on Knee Health
Ignoring tendonitis can harm your knee health over time. Pain and avoiding movement can lead to chronic knee problems. This increases the chance of getting osteoarthritis and other serious conditions.
It’s important to take action early to protect your knee. This helps keep you mobile and prevents more injuries.
Diagnosis of Knee Tendonitis

When you notice symptoms of knee tendonitis, the diagnosis process is key. First, your doctor will ask about your medical history. They want to know about your symptoms and how they affect your daily life. Then, they will do a physical exam to check your knee and find any tender spots or swelling.
Imaging tests are vital for diagnosing knee tendonitis. X-rays rule out bone problems that might be causing the pain. They show if there are fractures. An ultrasound uses sound waves to spot tears in the patellar tendon. For more detailed views, an MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to show tendon changes.
After diagnosing knee tendonitis, you can talk about treatment. Usually, starting with physical therapy is suggested. This includes exercises to stretch and strengthen your knee. You might also take pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium to help with pain.
Knowing how knee tendonitis is diagnosed helps you take care of your knee better. If you have ongoing pain, see a doctor. Early treatment can stop more serious problems from happening.
| Imaging Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|
| X-ray | To exclude other bone issues causing knee pain |
| Ultrasound | To visualize tears in the patellar tendon |
| MRI | To identify subtle changes in the tendon |
Treatment Options for Seniors with Knee Tendonitis

Older adults with knee tendonitis can find relief through various non-operative treatments and rehabilitation. These methods help ease pain, improve function, and keep the knee healthy.
Non-operative Treatment Approaches
Non-operative treatments are key in managing knee tendonitis. They include:
- Rest: Giving the knee time to heal by avoiding painful activities.
- Ice therapy: Using ice packs to reduce swelling and ease pain.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Taking medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage pain.
- Activity modification: Changing daily activities to reduce knee strain.
Keeping a healthy weight is also important for knee health. Losing just 10 pounds can help reduce knee pain and slow arthritis. Regular, low-impact exercises are vital for joint health and pain reduction.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is essential for treating tendonitis. It offers exercises to strengthen knee muscles and improve flexibility. A structured rehabilitation program can lead to:
- Improved muscle strength: Strengthening exercises can reduce knee pain by 25%.
- Enhanced mobility: Low-impact activities like walking and swimming improve joint function.
- Long-term relief: About 60% of older adults see better knee function after rehab.
In summary, combining non-operative treatments with physical therapy helps manage knee tendonitis in seniors. This approach promotes better health and quality of life.
Managing Tendonitis in Older Adults
Managing tendonitis in older adults needs a full plan. Start with rest and slow returns to activities. Use ice packs to reduce swelling and help healing.
Controlled movements, guided by experts, keep you moving without making things worse. Regular check-ups with your doctor are key. They help keep your treatment on track.
A healthy diet is also important. Eat foods rich in omega-3s, like fish, and drink plenty of water. This helps your tendons heal faster.
Adding knee health tips to your routine helps too. Try to lose weight to ease knee pressure. Even a little weight loss can make a big difference.
Doing moderate exercise for 30 minutes, three times a week, also helps. It’s good for your joints, even if only 20% of people with arthritis do it.
Preventive Measures for Senior Knee Health
Keeping your knees healthy is key as you get older. Doing exercises that target the knee is vital. It helps strengthen the joint and lowers injury risk. This way, you can stay active and enjoy life more.
Exercises to Strengthen Knee Joint
Adding certain exercises to your routine can boost knee health. Low-impact activities are best because they’re easy on the knees. Here are some great ones:
- Walking: A gentle way to activate leg muscles without excessive force.
- Swimming: Offers resistance to strengthen muscles and improve joint stability.
- Stationary biking: A recumbent bike is very kind to the knees.
- Strength training: Focuses on exercises that enhance the strength of muscles surrounding the knee.
- Flexibility routines: Stretching maintains joint flexibility and reduces stiffness.
Tips for Injury Prevention
Preventing injuries is key for keeping your knees healthy. Follow these tips to lower your risk of painful conditions:
- Wear appropriate footwear with good support to prevent instability.
- Practice proper body mechanics during daily activities to reduce strain on your knees.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to minimize inflammation.
- Engage in regular health screenings with your healthcare provider to tailor your prevention plan.
- Be mindful of warm-up and cool-down routines to help prevent injuries.
By adding these exercises and tips to your routine, you’ll set a strong foundation for knee care. Taking proactive steps can improve your knee health. This way, you can stay active and enjoy life in your golden years.
Conclusion
Knee tendonitis in seniors is a big worry that can really hurt your daily life. As you get older, you’re more likely to face this problem. About 25% of people over 55 get persistent knee pain in a year.
This shows how important it is for seniors to know about knee health. We need to find better ways to handle this common issue.
Knowing the signs, reasons, and treatments for tendonitis is key for seniors. It’s not just about pain; it can also cause serious problems if ignored. By taking care of your knees and working with doctors, you can stay active and avoid serious injuries.
Looking after your knee health is vital as you age. Being proactive helps keep your joints strong and healthy. This way, you can fight off the effects of aging on your muscles and bones.
** Our website contains affiliate links. This means if you click and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission. Don’t worry, there’s no extra cost to you. It’s a simple way you can support our mission to bring you quality content.
FAQ
What is tendonitis, and how does it affect seniors?
Tendonitis is when the tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. It often hits the knees in seniors due to wear and tear. This leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility.
What are the common symptoms of knee tendonitis in seniors?
Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and swelling around the knee. These symptoms get worse with activity or after sitting for a while.
What causes knee tendonitis in older adults?
It’s caused by aging, repeated stress, and overexertion. Obesity and joint problems also play a part. Walking, running, or climbing stairs can trigger it.
How can knee tendonitis impact daily activities for seniors?
It limits mobility and makes daily tasks hard. It affects bending, walking, and standing. This can reduce social and physical activity.
What diagnostic methods are used for knee tendonitis?
Doctors use a detailed medical history, physical exam, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. These help check tendon damage and rule out other issues.
What treatment options are available for managing tendonitis in seniors?
Treatments include rest, ice, pain relievers, and physical therapy. Exercises help strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
How can seniors effectively manage tendonitis?
Managing it means resting, using ice, and avoiding too much strain on the knee. Regular health check-ups help adjust treatment plans.
What preventive measures can seniors take to avoid knee tendonitis?
Seniors should do low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling. This strengthens joints without too much strain. Paying attention to body mechanics and wearing the right shoes also helps prevent injuries.

“This article does a great job of explaining how tendonitis affects seniors’ knees. One question I have is: what are the best low-impact exercises to help with recovery? From my experience, gentle stretching and swimming have been helpful in reducing knee pain. I also think more awareness is needed about how early intervention can prevent worsening symptoms. Has anyone found specific treatments or therapies particularly effective?”
Hi Robbie,
Thank you for your thoughtful comment! I’m glad you found the article helpful. You’re absolutely right—gentle stretching and swimming are excellent low-impact exercises for tendonitis recovery. Other great options include cycling, seated knee extensions, and water aerobics, which help strengthen the muscles around the knee without putting too much stress on the joints.
I completely agree that raising awareness about early intervention is crucial in preventing worsening symptoms. As for effective treatments, many people find physical therapy, massage therapy, and the use of supportive braces beneficial. Has anyone else had success with specific treatments? I’d love to hear more experiences! ????
Cheers
John
Tendonitis in seniors is a serious yet often overlooked issue that significantly impacts knee health and mobility. Many older adults mistakenly attribute knee pain to aging, not realizing that tendonitis is a treatable condition. This article does an excellent job of breaking down the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee tendonitis in seniors. Early diagnosis is crucial since misdiagnosing it as arthritis can lead to inadequate treatment and prolonged discomfort. Non-surgical treatments, including rest, ice therapy, and physical therapy, can provide significant relief. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming and walking can help prevent tendonitis from developing. Seniors should be aware of how their daily habits and activities contribute to knee stress and take proactive steps to protect their joints. Addressing tendonitis early ensures better mobility and quality of life, allowing older adults to stay active and independent for longer. Seeking medical advice for persistent knee pain is always a wise step.
Hi Andrejs,
Thank you for your thoughtful and insightful comment! You’ve highlighted a crucial point—many seniors assume knee pain is just a part of aging when, in reality, tendonitis is a treatable condition. Early diagnosis and proper management can make a huge difference in maintaining mobility and quality of life. I completely agree that proactive steps, like low-impact exercises and maintaining a healthy weight, play a vital role in prevention and recovery.
I appreciate you emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice for persistent pain—it’s always best to get a proper diagnosis to ensure the right treatment approach. Thanks again for your valuable input! ????
Cheers
John